by Cortney Sieben, Engineering Process Manager
In the fast-evolving field of curtainwall construction, Building Information Modeling (BIM) has emerged as a transformative tool for enhancing project efficiency, reducing errors, and improving collaboration among trade partners, architects, and general contractors. This paper explores various trends and strategies in BIM coordination within the curtainwall industry, aiming to provide comprehensive insights into how Enclos leverages BIM to streamline processes and achieve superior project outcomes.
Industry Trends in BIM Coordination
To Enclos, BIM coordination is more than just a contractual obligation. It is critical to overall project success. With recent trends in accelerated project schedules, ensuring effective front-end coordination is paramount. From project inception, BIM coordination establishes alignment among all parties, internal and external.
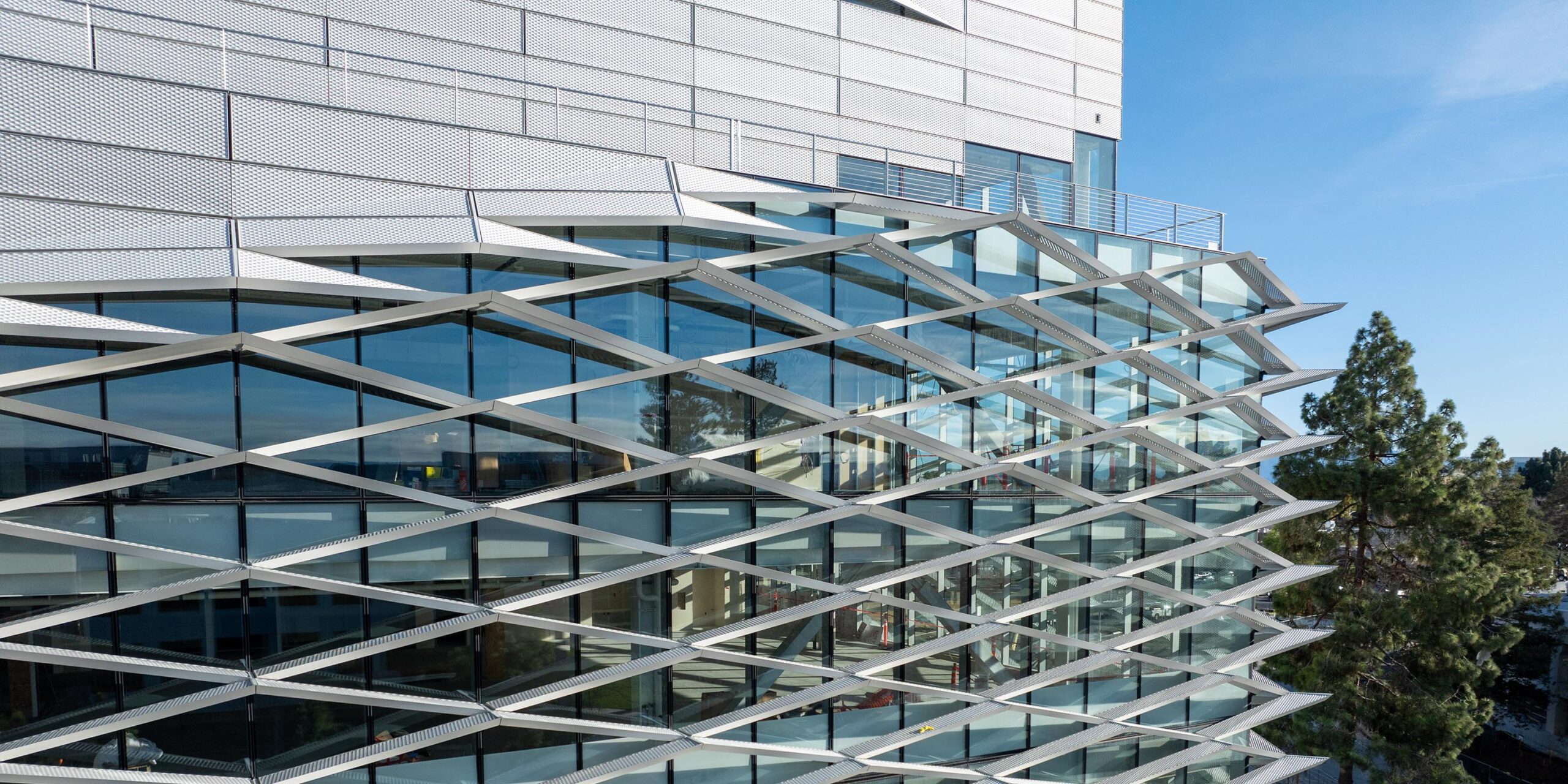
Our strategy for managing BIM coordination starts with low-level detail modeling and continues with progressive refinement throughout the project life cycle. Beginning with a highly accurate but simplistic conceptual model, detail is added as the project progresses, ending with a high-level detail model for closeout delivery. A phased approach ensures that initial conceptual designs are robust enough to guide subsequent detailed design, fabrication, construction, maintenance, and replacement phases. Ten years ago, there were many tall, angular buildings in the curtainwall industry. Current market trends of unique, curved, and complex building forms make coordinating with BIM models the most effective method. Utilizing the latest industry technology and computational modeling to optimize complex building skins keeps Enclos at the forefront of the custom curtainwall industry.
A recently completed facade showcases how computational modeling can transform BIM development, offering a glimpse into the potential of innovative building design. The facade featured a cold-warped glass system to give the wall the appearance of an undulating wave. Enclos utilized Rhino and Grasshopper to evaluate its cold-warped glass system, determining the necessary cold form bending while ensuring it stayed within structural performance limits. The analysis can be performed efficiently by using basic geometry to model the system, such as a simple warped surface representing the glass. Once validated, further details can be incorporated to advance the process.
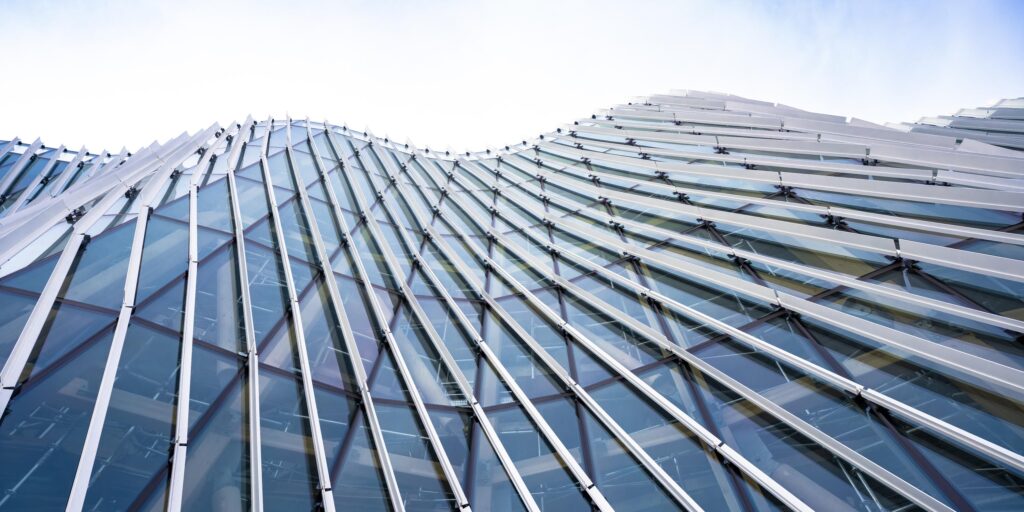

During the design-assist phase of a project, it is not uncommon for Enclos to work with the architect to optimize these building systems using parametric modeling. Parametric modeling allows many design options to be assessed and evaluated quickly and efficiently. Identifying the optimal parameters early in the project lifecycle enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and improves cost-effectiveness. These models follow through to the project’s post-sale design coordination and installation. By setting clear expectations and integrating BIM as a planning tool from the outset, Enclos enhances project predictability and minimizes costly rework.
BIM as a Communication Tool
BIM’s role extends beyond its traditional use as a design and documentation tool—it serves as a powerful communication medium throughout the curtainwall project lifecycle. Externally, BIM facilitates the tracking and scheduling of production and installation activities. It aids in coordinating material handling logistics, optimizing erection aids and crane usage, and ensuring seamless integration with onsite construction processes. This real-time visibility into project progress and logistics helps mitigate delays and enhances overall project efficiency.
Internally, BIM models function as dynamic repositories of project status and information. They are a central hub for sharing updates and revisions among multidisciplinary teams involved in design development, fabrication detailing, and installation sequencing. This transparency fosters collaboration and enables proactive decision-making, reducing conflicts and delays during critical project phases.
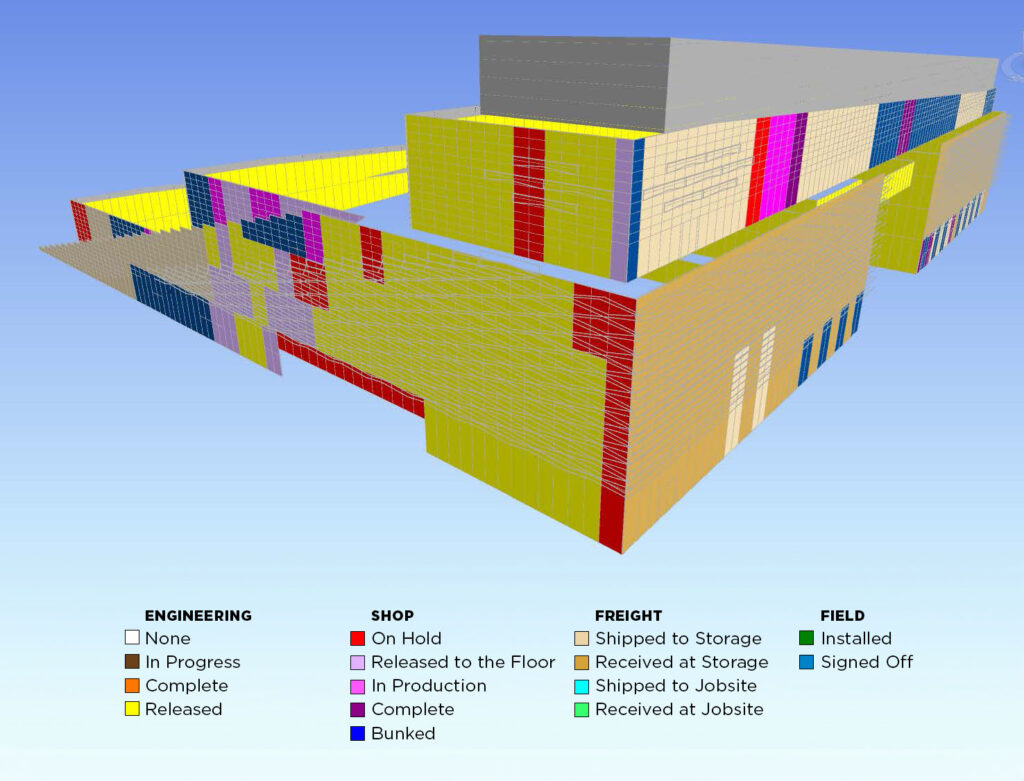
For another recent project, Enclos created a “status model,” or a simplified model of the facade that identified every location where a curtainwall unit would be installed. Each location called an “address,” was assigned a unique identifier with information about the unit. We monitor each unit’s progress through engineering, manufacturing, shipping, and installation. Enclos’ proprietary software and internal database link the assigned progress to the BIM surface mode, displaying each unit’s live, color-coded representation. This “status model” allows us to visually track the status of each unit in the 3D model. The model can then be accessed in Navisworks by anyone on the engineering, shop, operations, or field teams to have the most current and accurate information, effectively communicating project deliverables internally and externally to owners, architects, and general contractors. This visual tool has proven highly effective for communication during high-level project meetings.
Several techniques assist in populating coordinates of each anchor condition, allowing field layout data to be delivered quickly and accurately. These tools include wireframe modeling (a form of simplistic modeling that defines the facade of a curtainwall as simple surfaces), modeling point data, and computational scripting using programs like Grasshopper. A simple point defined by an X, Y, and Z coordinate can represent an exact onsite location reference. A crucial aspect of BIM coordination is integrating with field and installation technology. In cases where traditional layout and installation methods are obsolete, BIM models provide 3D point data and IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) representing the visual geometry to the Total Station layout device used for field surveying, ensuring high precision in complex building layouts.
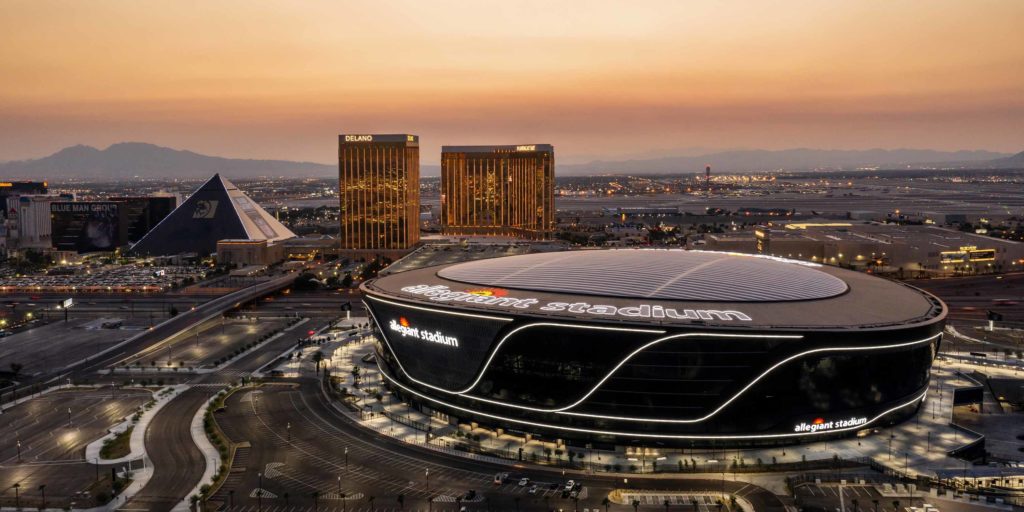
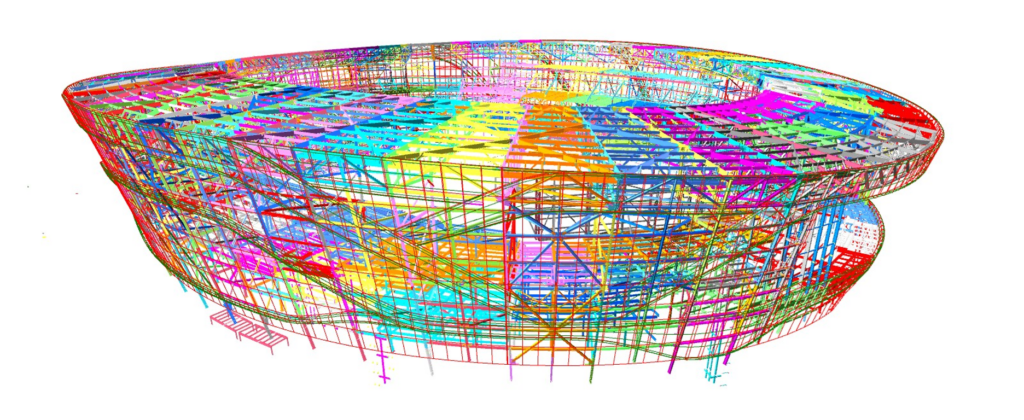
The Las Vegas NFL Stadium exemplifies the transformative power of BIM data, setting a new standard for leveraging digital tools in modern architecture. The project had a few design challenges, including complex geometry, layouts, and a BIM 500 requirement. Due to the project’s three-phase post-tensioning approach during erection, Enclos used the Total Station to scan and relay data for as-built building positioning back to our models. This allowed analysis of the anchors’ final positioning based on the structure’s as-built positioning. Whole sections of building anchor positions could be scanned onsite, sent to the model, evaluated, adjusted, and returned to the field quickly and efficiently. Communicating essential property data from BIM models into centralized databases enhances project management efficiency and supports informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.

Clash Coordination & Transitioning to Cloud-Hosted Models
The transition to cloud-hosted BIM models represents a significant advancement in clash coordination within the curtainwall industry. Real-time accessibility allows all project players to collaborate seamlessly regardless of geographic location. This accessibility to live data enables immediate decision-making and facilitates agile responses to emerging project challenges.
Various coordination platforms, such as Accela, BIM360, Revizto, Procore, Navisworks, and PlanGrid, offer flexibility in clash detection and resolution. The various coordination platforms are adapted to different phases of construction documentation. From initial design development through fabrication and onsite construction, each platform provides unique features that cater to specific project needs, ensuring that clashes are identified and resolved efficiently to prevent costly rework during construction. We must adapt and accommodate the various platforms as we work with a wide range of partners. Exposure to various coordination platforms has allowed us to identify new methods to increase productivity and organization.
Coordinating among numerous trade partners presents challenges due to the various model formats, file sizes, and manual consolidation of models required for each trade. Emerging technologies help simplify many of these issues. Revizto is one platform gaining traction as a coordination standard. It manages coordination between numerous trade partners using cloud-hosted models that are compressed for quick reference and consolidated in a central location. Models are automatically synced on schedule, typically weekly, by all trade partners. We are seeing a trend to rely more on the live model for up-to-date design information. While contract documents still reign, there have been benefits to having access to real-time cloud-hosted models that are often revised before an officially published version of the drawings. The challenge becomes determining what documents should be followed and when. With accelerating project schedules, there are times when the team must make a judgment call on when it is appropriate to use a more up-to-date model over the published contract documents.
Responsibility for clash detection has evolved significantly within Enclos projects. Previously relegated to the later stages of design or even during construction, clash detection now occurs earlier in the project timeline during the design-assist phase. This proactive approach ensures that potential conflicts between structural elements, mechanical systems, and architectural features are addressed before fabrication or in alignment with shop drawing preparation. BIM clash software like Revizto allows trade partners to assign clashes with adjacent trades. Once a clash is assigned, it is actively monitored through meetings, comments, pictures, and model designations. A clash can only be closed out once the clash creator evaluates and approves a resolution, ensuring trade alignment. This tracking process documents responsibility for the entire timeline of the project with all involved parties. General contractors play a crucial role in overseeing clash coordination between trades, such as resolving conflicts between steel structures and architectural components. This oversight helps facilitate smoother construction progress and minimizes onsite disruptions.
Conclusion
BIM coordination represents a transformative shift in the curtainwall industry, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance project management, collaboration, and efficiency. Enclos’ strategic approach to BIM integration—from prioritizing front-end coordination, utilizing computational modeling for efficiency, and embracing cloud-hosted models for clash coordination—underscores its commitment to delivering superior project outcomes.
Looking forward, technological advancements and collaborative practices promise to further refine BIM’s role in optimizing construction processes and overcoming industry challenges. By embracing these trends and strategies, stakeholders in the curtainwall industry can navigate complexities with greater confidence, ensuring the successful delivery of projects that meet and exceed client expectations.
